CURRENT ISSUE
Click on the cover to view as a virtual edition:
FEBRUARY 2026
Click on the cover to view as a virtual edition:
FEBRUARY 2026
To see back issues, please click here.
MEDIA PACK
To download a PDF copy of the 2026 SPN media pack, click here.
For forward features information, click here.
To discuss advertising within SPN, please call Tony Weston on +44 (0)1474 813433 or to email him, click here.
To download a PDF copy of the 2026 SPN media pack, click here.
For forward features information, click here.
To discuss advertising within SPN, please call Tony Weston on +44 (0)1474 813433 or to email him, click here.
SUBMIT NEWS
To submit a news story or press release about your company, please click here.
PLEASE NOTE: When submitting, please ensure any image sent is high resolution.
To submit a news story or press release about your company, please click here.
PLEASE NOTE: When submitting, please ensure any image sent is high resolution.
LATEST NEWS
 Dryden Aqua Report - UV irradiation in swimming pools
Dryden Aqua Report - UV irradiation in swimming pools
By Dr Howard T Dryden
Dryden Aqua manufacture UVc low pressure irradiation system for the treatment of water in the aquarium and aquaculture industry. However we have made a policy decision not to use UV for aquarium and aquaculture recirculation systems, or recycled water in swimming pools. The reasons for this decision are detailed in this report.
Disinfection by-products
Medium pressure UV is very effective for the dechloramination of swimming pool water; but by its very nature UV does not have any residual, so it cannot be substituted for the use of chlorine. Chlorine will react with ammonium to form inorganic complexes such as monochloramine, dichloramine and trichloramine (nitrogen trichloride).
Nitrogen trichloride is very volatile gas and will tend to come out of solution into the atmosphere to give pools their characteristic chlorine smell. Nitrogen trichloride is not lipid soluble so it is not absorbed by your skin, and when you breathe in the gas, it will not enter your blood stream. However nitrogen trichloride is acidic, and an irritant with the potential to cause lung damage. France is the only country in Europe that has set limits for the concentration of nitrogen trichloride in the atmosphere. French decree 2003-110 of the 11/02/2003 & EA4 2008-65 2008 recognizes nitrogen trichloride as an occupational disease and that the atmospheric concentrations should be monitored. In accordance to the French decree, when UVc irradiation is used for dechloramination the THM chloroform atmospheric concentration also has to be monitored at least twice a year.
The UK does not have any WEL (work exposure level) for nitrogen trichloride in the atmosphere of a pool building. The UK Health & Safety Executive (HSE) state that it is the responsibility of the pool operator to prepare a COSHH risk assessment, and if the gas is considered a risk, then a limit must be established. Given that there are no limits in the UK it would seem reasonable to adopt the French position of 0.5mg/m3 as an upper limit. The same situation must also apply to THM`s in the atmosphere. The French government has established that there is a risk, so it now becomes the responsibility of all UK pool operators to comply with their health and safety obligations and monitor THM concentrations in the atmosphere when UVc irradiation is used to treat the water.
Professor Blatchely (2009 World Aquatic Health Conference) of Purdue University has compared DPD analysis for combined chlorine against the laboratory technique of MIMS (membrane inlet mass spectrometer) and found that DPD chemical analysis used by most swimming pools gave a reading 3 times higher than MIMS for inorganic chloramines. This result is not new and was first reported by Dr Palin 50 years ago that DPD analysis was subject to interference from organo-chloramines.
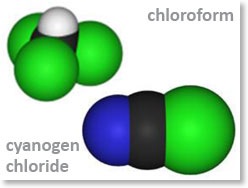
The end product of UVc irradiation of nitrogen trichloride will be nitrogen gas and chloride, these products are completely safe and do not represent a hazard. However at least 75% of the chloramines are organic molecules, the oxidation end product is CO2 carbon dioxide, which is completely safe, but the intermediate chemicals formed are the next smallest molecules that include chloroform and cyanogen chloride. The Henry`s constant for both these molecules tells us that they are volatile and will escape the water into the atmosphere, and this is why we have the French decree that states chloroform must be monitored in the atmosphere whenever UVc irradiation is employed.
The French decreed did not include cyanogen chloride; the main reason for this decision is that it is unstable and difficult to measure. However given that the maximum exposure level from the UK HSE is only 0.77 mg/m3 for 15 minutes and the concentration can reach 0.14 mg/l in pool water after UVc, Dryden Aqua consider this gas emission to be of serious concern. It would only take 5 liters of water to degas into the atmosphere to make several square meters of pool area exceed the upper 15 minutes exposure level. If a class of children were to jump into a pool with 500,000 liters of water at 0.14mg/l it might be expected that the cyanide gas levels could exceed the upper exposure level in the entire building for more than 30 minutes. Dryden Aqua in association with the SETN (Scottish Environmental Technology Network) is working on the water and air analytical techniques for cyanide in swimming pools. The data will be published over the next 12 months, suffice to say the results are of concern and we need to reduce the amount of chlorine used by swimming pools. This has been the focus of Dryden Aqua R&D and the development of our pool water treatment products.
The literature and reports published on UV irradiation are conflicting, some claim a problem and others state that the technology is safe and does not form THMs. In some cases there may be vested interests, especially if the reports are by UVc manufacturers. The fact is that trials can be set up and monitoring regimes established to give good or not so good results. The concentration of THMs will depend upon the time of day, and loading in the pool. Also if the level of dissolved organics is reduced to a minimum by activated carbon, if peroxide is injected into the water or if there are water cannon, flumes or fountains in the system to degas the water, under these conditions you will achieve low levels of THMs in solution. The basic chemistry dictates that chloroform and cyanogen chloride will form, and the gas will either be in solution or in the air and this just reinforces the French position than you need to monitor the condition to insure compliance with your health and safety obligations.
UV and photolysis of chlorine and carbon cost
It is well established that the UV component of sunlight will cause the photolysis of chlorine and reduce it back to chloride. This is why cyanuric acid is used in out-door pools to try and protect the chlorine. Medium pressure UV lamps irradiate a range of UV wavelengths that will also cause photolysis of chlorine. The degree of photolysis will depend upon the water quality, light wavelengths and energy transmitted. In pools measured by Dryden Aqua with UV irradiation units turned on, a pool will use between 2 and 4 times as much chlorine. This is simple to confirm, just turn off the unit and measure the chlorine consumption, and then turn it back on again.
With the UV systems, more chlorine is consumed and more acid will be required to buffer the system. The UVc unit will have a power demand, again this depends upon the size of the unit, but typically it will be between 5 and 10 kw at a cost of up to £8,000 for power.
UV lamps usually need to be changed once a year, and the quarts glass every few years, with some installation there are considerable service costs that could amount to more than £15,000 per annum The environmental and economic case for UV irradiation should be given consideration by the pool operator.
Bio-hazard risk
During spring 2011 there was a serious disease out-break caused by multi drug resistant E.coli in Germany. It is believed that the source of the infection was initially cucumbers from Spain but now it is believed to be more likely the source of the infection was bean-sprouts or similar produce grown in a hydroponic recycle systems. UV irradiation can give a very high bacteria and virus kill level.
However not all organisms will be killed and some will actually repair the damage to their DNA. Even if only 1 in 10 billion bacteria or a virus survive the UV, by a process of natural selection, when water is recycled bacteria will evolve in the system that can tolerate the level of UV irradiation, nature always finds a way to survive. UVc irradiation is employed in many hydroponic recycle systems.
In 1997, Dr. R.E. Hurlbert of Washington State University reported that genetically modifying E. coli to make a natural biological weapon is not difficult by “randomly induced spontaneously or classical mutagenic procedures e.g. exposure to UV or X-ray irradiation” It is unlikely that a swimming pools will produce a genetically modified super-bug because the concentration of chlorine should be sufficient to prevent the survival of a planktonic bacteria. This is a very good reason for the continued use of chlorine in both private and public pools. However viri are a different matter, they generally have a much higher tolerance than bacteria to UV and chlorine. It is therefore conceivable that UVc irradiation of recycled pool water could create a genetically modified human pathogenic virus from something as benign as the common cold and turn it into a disease risk for the pool staff or even a pandemic flu.
Dryden Aqua are marine biologists, and in the aquaculture industry the policy is to avoid any process or chemical that may cause a problem if an alternative solution is available. In the swimming pool industry the reverse appears to be true, the potential risks need to be fully quantified and analyzed before a decision is reached. The problem is, it is just about impossible to quantify risks so decisions can never be concluded, for this reason it is very important to have standards such as the German DIN that provide a formal framework. Given the absence of standards in the UK, Dryden Aqua have developed PAWS (pool air & water standard) www.swimmingpaws.com and an integrated water treatment system design in order to comply with PAWS.
Final comments
It is not reasonable to expect pool operators to understand “work exposure levels” toxic thresholds or to prepare detailed risk assessments relating to water treatment systems. Neither should it be the responsibility of companies or manufacturers of equipment with a vested interest in the technology. In this respect Dryden Aqua are no exception, we have a vested interest to promote our technology, however we also like to think that we have an ethical conscious and if we are aware of a problem or a potential hazard then we will not promote the technology and we will alert the industry.
In order allow pool operators to comply with their health and safety obligations and to help them optimize their swimming pools systems we have now developed a neurological program on our secure server that pool operators may use to enter their water and air quality data. The system will record and display the results and will provide advice for the pool operator how to optimize the performance and safety of their swimming pool. This is a free service provided by Dryden Aqua, for more information visit their website: www.drydenaqua.com
<< Back to home

By Dr Howard T Dryden
Dryden Aqua manufacture UVc low pressure irradiation system for the treatment of water in the aquarium and aquaculture industry. However we have made a policy decision not to use UV for aquarium and aquaculture recirculation systems, or recycled water in swimming pools. The reasons for this decision are detailed in this report.
Disinfection by-products
Medium pressure UV is very effective for the dechloramination of swimming pool water; but by its very nature UV does not have any residual, so it cannot be substituted for the use of chlorine. Chlorine will react with ammonium to form inorganic complexes such as monochloramine, dichloramine and trichloramine (nitrogen trichloride).
Nitrogen trichloride is very volatile gas and will tend to come out of solution into the atmosphere to give pools their characteristic chlorine smell. Nitrogen trichloride is not lipid soluble so it is not absorbed by your skin, and when you breathe in the gas, it will not enter your blood stream. However nitrogen trichloride is acidic, and an irritant with the potential to cause lung damage. France is the only country in Europe that has set limits for the concentration of nitrogen trichloride in the atmosphere. French decree 2003-110 of the 11/02/2003 & EA4 2008-65 2008 recognizes nitrogen trichloride as an occupational disease and that the atmospheric concentrations should be monitored. In accordance to the French decree, when UVc irradiation is used for dechloramination the THM chloroform atmospheric concentration also has to be monitored at least twice a year.
The UK does not have any WEL (work exposure level) for nitrogen trichloride in the atmosphere of a pool building. The UK Health & Safety Executive (HSE) state that it is the responsibility of the pool operator to prepare a COSHH risk assessment, and if the gas is considered a risk, then a limit must be established. Given that there are no limits in the UK it would seem reasonable to adopt the French position of 0.5mg/m3 as an upper limit. The same situation must also apply to THM`s in the atmosphere. The French government has established that there is a risk, so it now becomes the responsibility of all UK pool operators to comply with their health and safety obligations and monitor THM concentrations in the atmosphere when UVc irradiation is used to treat the water.
Professor Blatchely (2009 World Aquatic Health Conference) of Purdue University has compared DPD analysis for combined chlorine against the laboratory technique of MIMS (membrane inlet mass spectrometer) and found that DPD chemical analysis used by most swimming pools gave a reading 3 times higher than MIMS for inorganic chloramines. This result is not new and was first reported by Dr Palin 50 years ago that DPD analysis was subject to interference from organo-chloramines.
The end product of UVc irradiation of nitrogen trichloride will be nitrogen gas and chloride, these products are completely safe and do not represent a hazard. However at least 75% of the chloramines are organic molecules, the oxidation end product is CO2 carbon dioxide, which is completely safe, but the intermediate chemicals formed are the next smallest molecules that include chloroform and cyanogen chloride. The Henry`s constant for both these molecules tells us that they are volatile and will escape the water into the atmosphere, and this is why we have the French decree that states chloroform must be monitored in the atmosphere whenever UVc irradiation is employed.
The French decreed did not include cyanogen chloride; the main reason for this decision is that it is unstable and difficult to measure. However given that the maximum exposure level from the UK HSE is only 0.77 mg/m3 for 15 minutes and the concentration can reach 0.14 mg/l in pool water after UVc, Dryden Aqua consider this gas emission to be of serious concern. It would only take 5 liters of water to degas into the atmosphere to make several square meters of pool area exceed the upper 15 minutes exposure level. If a class of children were to jump into a pool with 500,000 liters of water at 0.14mg/l it might be expected that the cyanide gas levels could exceed the upper exposure level in the entire building for more than 30 minutes. Dryden Aqua in association with the SETN (Scottish Environmental Technology Network) is working on the water and air analytical techniques for cyanide in swimming pools. The data will be published over the next 12 months, suffice to say the results are of concern and we need to reduce the amount of chlorine used by swimming pools. This has been the focus of Dryden Aqua R&D and the development of our pool water treatment products.
The literature and reports published on UV irradiation are conflicting, some claim a problem and others state that the technology is safe and does not form THMs. In some cases there may be vested interests, especially if the reports are by UVc manufacturers. The fact is that trials can be set up and monitoring regimes established to give good or not so good results. The concentration of THMs will depend upon the time of day, and loading in the pool. Also if the level of dissolved organics is reduced to a minimum by activated carbon, if peroxide is injected into the water or if there are water cannon, flumes or fountains in the system to degas the water, under these conditions you will achieve low levels of THMs in solution. The basic chemistry dictates that chloroform and cyanogen chloride will form, and the gas will either be in solution or in the air and this just reinforces the French position than you need to monitor the condition to insure compliance with your health and safety obligations.
UV and photolysis of chlorine and carbon cost
It is well established that the UV component of sunlight will cause the photolysis of chlorine and reduce it back to chloride. This is why cyanuric acid is used in out-door pools to try and protect the chlorine. Medium pressure UV lamps irradiate a range of UV wavelengths that will also cause photolysis of chlorine. The degree of photolysis will depend upon the water quality, light wavelengths and energy transmitted. In pools measured by Dryden Aqua with UV irradiation units turned on, a pool will use between 2 and 4 times as much chlorine. This is simple to confirm, just turn off the unit and measure the chlorine consumption, and then turn it back on again.
With the UV systems, more chlorine is consumed and more acid will be required to buffer the system. The UVc unit will have a power demand, again this depends upon the size of the unit, but typically it will be between 5 and 10 kw at a cost of up to £8,000 for power.
UV lamps usually need to be changed once a year, and the quarts glass every few years, with some installation there are considerable service costs that could amount to more than £15,000 per annum The environmental and economic case for UV irradiation should be given consideration by the pool operator.
Bio-hazard risk
During spring 2011 there was a serious disease out-break caused by multi drug resistant E.coli in Germany. It is believed that the source of the infection was initially cucumbers from Spain but now it is believed to be more likely the source of the infection was bean-sprouts or similar produce grown in a hydroponic recycle systems. UV irradiation can give a very high bacteria and virus kill level.
However not all organisms will be killed and some will actually repair the damage to their DNA. Even if only 1 in 10 billion bacteria or a virus survive the UV, by a process of natural selection, when water is recycled bacteria will evolve in the system that can tolerate the level of UV irradiation, nature always finds a way to survive. UVc irradiation is employed in many hydroponic recycle systems.
In 1997, Dr. R.E. Hurlbert of Washington State University reported that genetically modifying E. coli to make a natural biological weapon is not difficult by “randomly induced spontaneously or classical mutagenic procedures e.g. exposure to UV or X-ray irradiation” It is unlikely that a swimming pools will produce a genetically modified super-bug because the concentration of chlorine should be sufficient to prevent the survival of a planktonic bacteria. This is a very good reason for the continued use of chlorine in both private and public pools. However viri are a different matter, they generally have a much higher tolerance than bacteria to UV and chlorine. It is therefore conceivable that UVc irradiation of recycled pool water could create a genetically modified human pathogenic virus from something as benign as the common cold and turn it into a disease risk for the pool staff or even a pandemic flu.
Dryden Aqua are marine biologists, and in the aquaculture industry the policy is to avoid any process or chemical that may cause a problem if an alternative solution is available. In the swimming pool industry the reverse appears to be true, the potential risks need to be fully quantified and analyzed before a decision is reached. The problem is, it is just about impossible to quantify risks so decisions can never be concluded, for this reason it is very important to have standards such as the German DIN that provide a formal framework. Given the absence of standards in the UK, Dryden Aqua have developed PAWS (pool air & water standard) www.swimmingpaws.com and an integrated water treatment system design in order to comply with PAWS.
Final comments
It is not reasonable to expect pool operators to understand “work exposure levels” toxic thresholds or to prepare detailed risk assessments relating to water treatment systems. Neither should it be the responsibility of companies or manufacturers of equipment with a vested interest in the technology. In this respect Dryden Aqua are no exception, we have a vested interest to promote our technology, however we also like to think that we have an ethical conscious and if we are aware of a problem or a potential hazard then we will not promote the technology and we will alert the industry.
In order allow pool operators to comply with their health and safety obligations and to help them optimize their swimming pools systems we have now developed a neurological program on our secure server that pool operators may use to enter their water and air quality data. The system will record and display the results and will provide advice for the pool operator how to optimize the performance and safety of their swimming pool. This is a free service provided by Dryden Aqua, for more information visit their website: www.drydenaqua.com
<< Back to home


















